- +(91) 98790 98103
- chestsurgeryassociates@gmail.com

Pleural Effusion
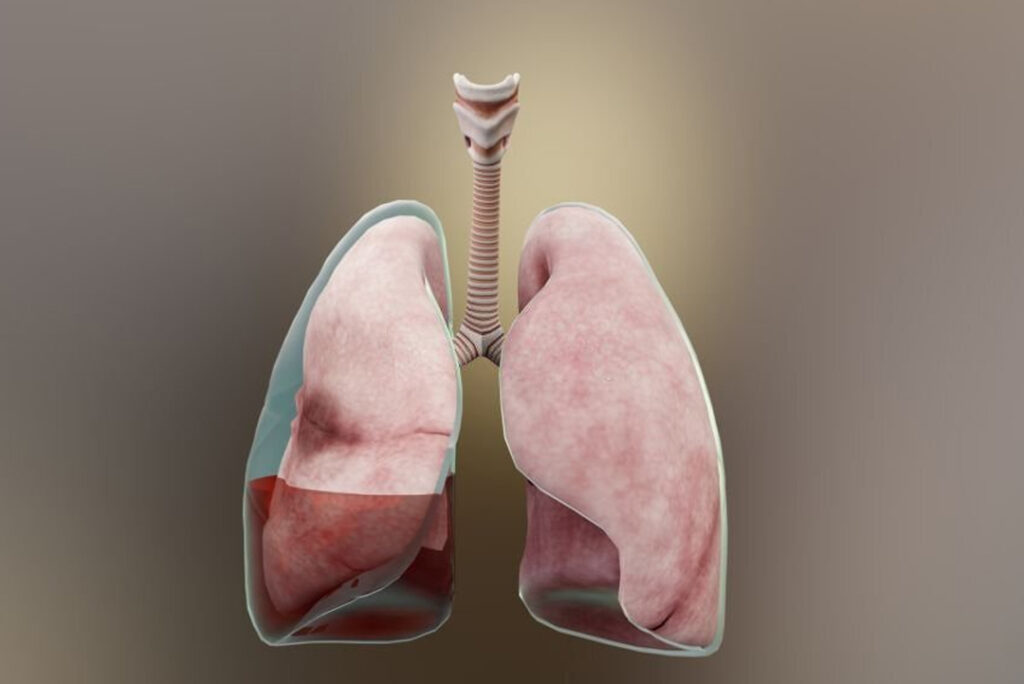
Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates between the two pleural layers, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs. Excessive amounts of such fluid can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs during ventilation.
Pleural Effusion (Fluid in the Lungs) is a condition with an abnormal collection of fluid in the Chest Cavity. The pleura is a thin membrane that lines the surface of the lungs and the inside of the chest wall outside the lungs. In pleural effusions, fluid accumulates in the space between the layers of pleura.
Excessive fluid may accumulate because the body does not handle fluid properly (such as in heart failure, or kidney and liver disease). The fluid or water in pleural effusions also may result from inflammation, such as in Pneumonia, Tuberculosis and many other conditions. In our country, Pneumonia and Tuberculosis are two of the commonest causes of Pleural Effusion.
Symptoms
- Shortness of Breath
- Chest Pain
- Cough
- Fever
Diagnosis
- Chest X-ray
- Ultrasound
- CT Scan
Treatment
Pleural Effusion due to tuberculosis is treated with Anti-tubercular Medicines. When the amount of pleural fluid is large and causing breathlessness, drainage of the fluid (Thoracentesis) is done to improve breathing. If it recurs again & again, a chest tube (or a pig tail catheter) may be inserted. Sometimes, the fluid becomes “Pus” and form a layer around the collapsed lung of forms multiple septations in the pus. This condition is now called “Empyema” (Pus around the Lungs) and need “Decortication” procedure.
Other Services
- Lung Cancer
- Thymoma (Myasthenia Gravis)
- Esophageal Cancer
- Hydatid Cysts
- Lung Nodules
- Pleural Effusion
- Pneumothorax
- Chest Wall Tumors
- Empyema
- Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Aspergilloma
- Chest Trauma Surgery
- Palmar Hyperhidrosis
- Tracheal Stenosis
- Tracheoesophageal Fistula
- Posterior Mediastinal Mass
- Bronchiectasis
- Chest Wall Deformities
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome